Thoracic outlet is a small space between the collarbone and 1st rib. The blood vessels and nerves that serve the arm are in this space. Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is the presence of hand and arm symptoms due to pressure against the nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet area.
There are three types: neurogenic (95%), venous (4%) and arterial (1%).
The main causes of TOS include: congenital 1st rib abnormalities, congenital extra rib, neck trauma, collarbone injury or repetitive stress from work.
Symptoms of TOS are:
Neurogenic: pain, numbness, weakness of the arm, neck pain.
Venous: pain, swelling, skin color changes (due to vein thrombosis).
Arterial: pain, coldness and pale discoloration.
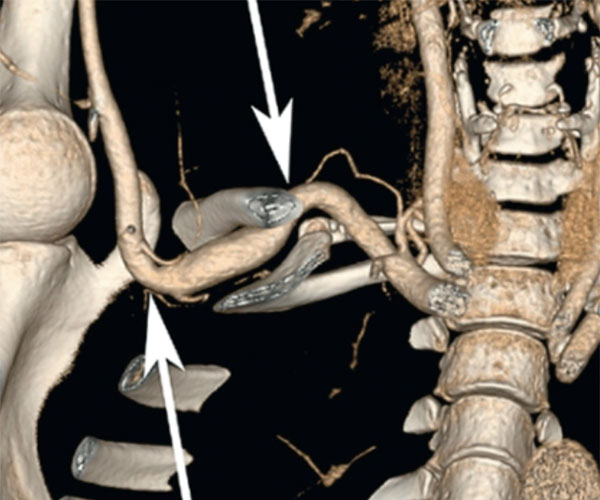
Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Treatment includes:
Neurogenic: physiotherapy is the initial treatment (which is successful in most of the cases). If symptoms persist surgical decompression is needed, usually by removing the first rib and certain muscles.
Venous: clot dissolving medication (thrombolysis) followed by blood thinners and then surgical decompression.
Arterial: surgical decompression and repair of the affected artery.
