Carotid arteries (right and left) are the main arteries to the brain.
The arteries are normally smooth and unobstructed on the inside. In some cases a sticky substance called plaque (atherosclerosis) builds up in the wall of the arteries. Risk factors are: age, family history, high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity and smoking. Atherosclerotic plaque of the carotid artery causes the artery to narrow and stiffen and is called carotid artery disease.
Carotid artery disease can cause a stroke (temporary or permanent). More commonly a piece of plaque breaks off and blocks a smaller artery of the brain. Sometimes the carotid artery itself is totally blocked by the plaque causing brain ischemia.
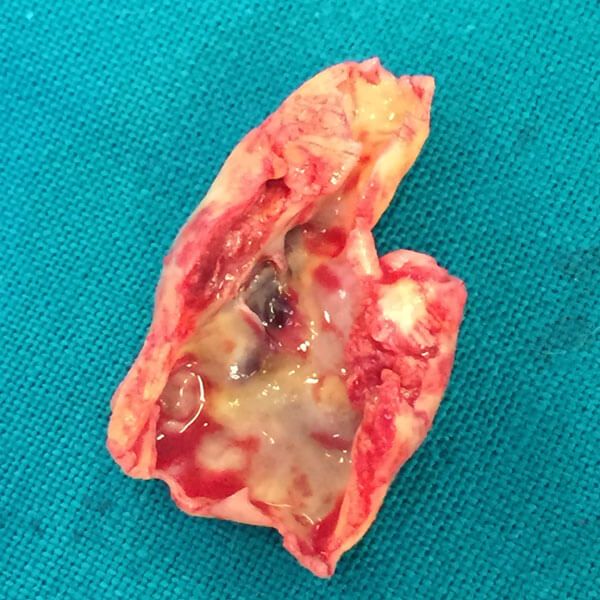
Carotid Plaque
Carotid artery disease may cause no symptoms. Unfortunately, the first sign could be a stroke (transient or permanent). The patient may experience weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, loss of vision in one eye or speech difficulty. If such symptoms occur, the patient should see a physician immediately.
Diagnosis of carotid artery disease is confirmed easily with Duplex Ultrasound. In some cases CT Angiography, MR Angiography or Contrast Angiography is needed to document the diagnosis.
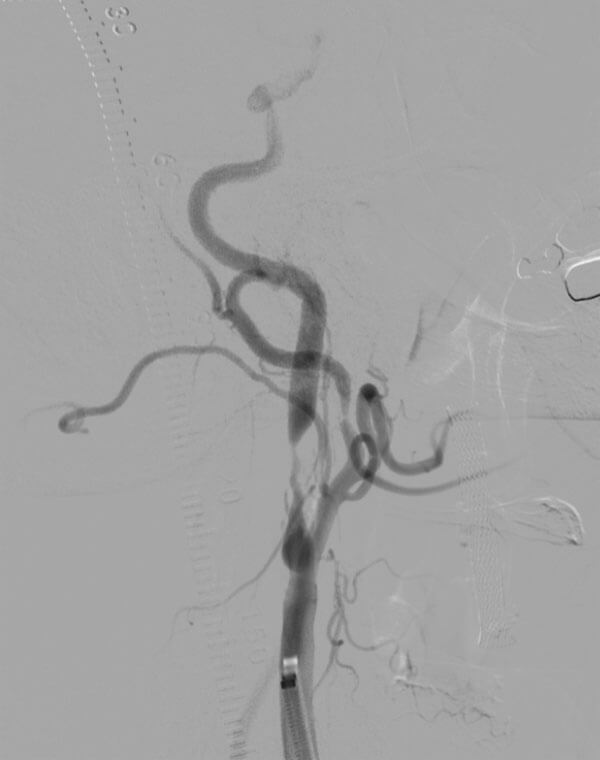
Carotid Artery Stenosis
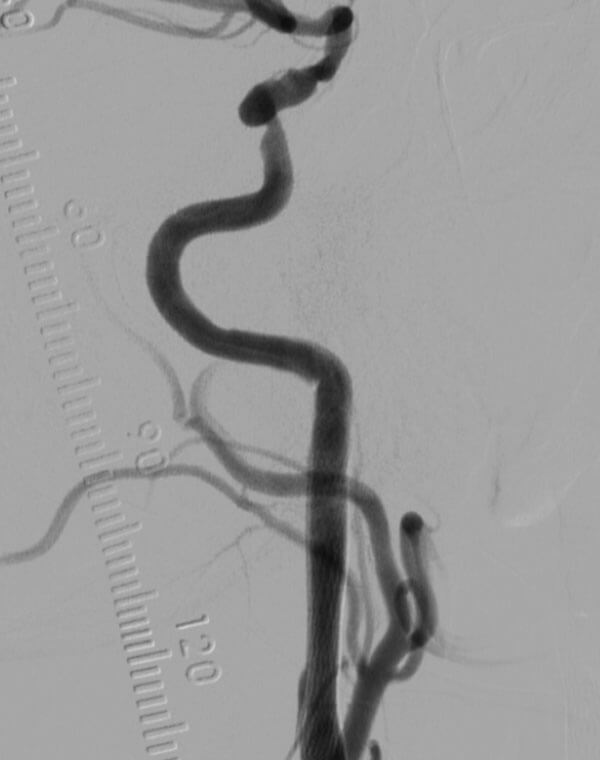
Carotid Stent
Treatment of carotid artery disease depends on symptoms and severity of narrowing. Besides medical therapy, invasive treatment, when needed, is performed with two methods. The first one is minimally invasive (angioplasty with or without stent). The second one is open surgical procedure.
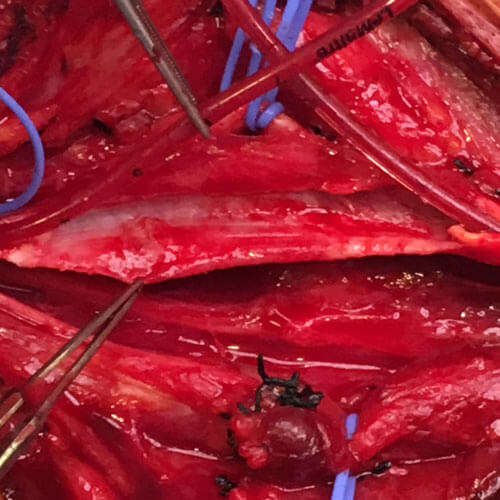
Carotid Endarterectomy
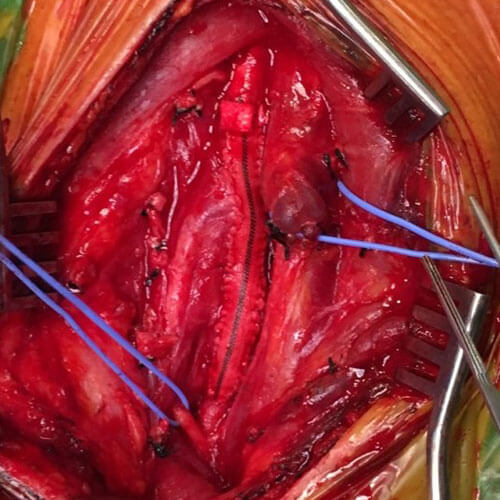
Patch Closure
During surgery, a neck incision is performed under general anesthesia and the plaque is removed from the artery.
For minimally invasive procedures, no incision is made and the repair of the artery is performed from within the vessel (this is why it is also called endovascular). Under local anesthesia, the vascular surgeon punctures the artery of the leg, uses a special filter to protect the brain and uses a special balloon to open the vessel. Finally a small metal tube (stent) is used to keep the artery open. The following day, the patient is discharged from the hospital and recovery is immediate without any pain.
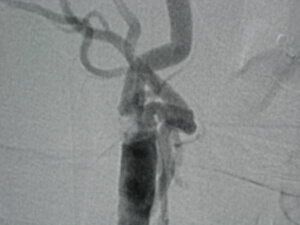
Carotid Artery Stenosis
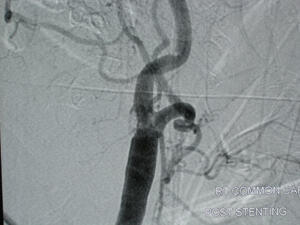
Carotid Artery Stent
For both methods there are indications and contradictions.
The results of both procedures are excellent when:
a) They are performed by experienced vascular surgeons in patients suitable for this technique.
b) They are performed in state of the art hybrid operating rooms which combine the safety of the operating room with the superb imaging capabilities of the angiography suite.
c) Last generation endovascular devices are used.
Patients with carotid artery disease should consult vascular surgeons with experience in both endovascular and open surgical repairs in order to receive the most appropriate method of treatment.
